BMS SYSTEMS PART-1
In This Article we are going to discuss about BMS systems complete working principles part 1
 |
| Air Handling Unit |
What is BMS :
- BMS means Building Management Systems, that provide control and monitoring of heating, air-conditioning, ventilation and other building services.
- BMS use programmable microprocessor based DDC (Direct Digital Control) Controllers communicating back to a Central Computer.
- Each of the controllers is programmed to meet the specific requirements.
- Controllers can also be used stand-alone for small Installations.
- BMS save energy and ensure optimal working environments and can deliver significant time and cost savings.
How to achieve ?
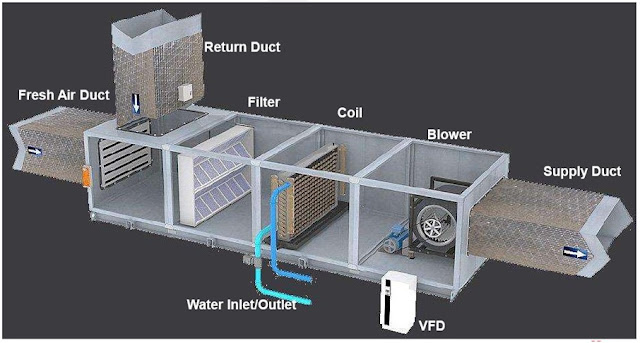
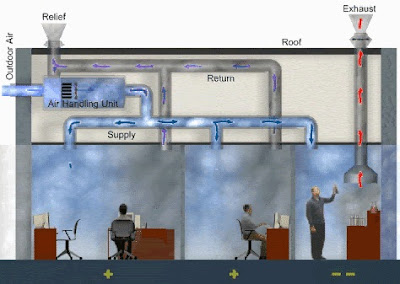
- Using AHU that means Air Handling Unit. This is the graphical view of Air Handling Unit.
- It consist of ( Fresh air duct , Return air duct , Exhaust air duct , Filter , coil , water inlet and outlet pipes , blower and so on).
- This is the schematic view of Air Handling Unit.
AHU:
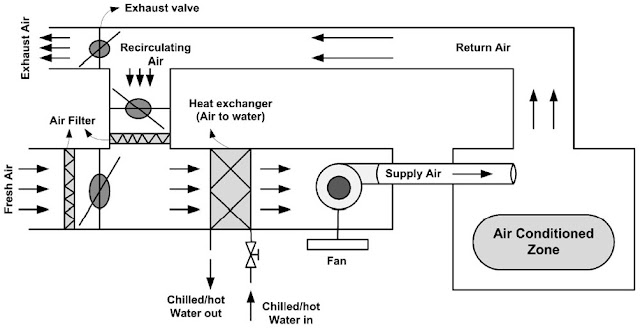
- An Air Handling Unit (AHU) is used to re-condition and circulate air as part of a heating, ventilating and air-conditioning system.
- The basic function of the AHU is to take in outside air, re-condition it and supply it as fresh air to a building. All exhaust air is removed, which creates an acceptable indoor air quality.
- Depending on the required temperature of the re-conditioned air, the fresh air is either heated by a recovery unit or heating coil or cooled by a cooling coil.
- In buildings where the hygienic requirements for air quality are lower, some of the air from the rooms can be re-circulated via a mixing chamber and this can result in significant energy savings.
- A mixing chamber has dampers for controlling the ratio between the return, outside and exhaust air.
- AHUs connect to duct work that distributes the conditioned air through the building and returns it to the AHU.
- A heat and cooling recovery exchanger is normally fitted
to the AHU for energy savings and increasing capacity. An AHU designed for
outdoor use, typically on roofs, is also known as a Roof Top Unit (RTU).
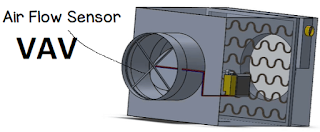
VAV:
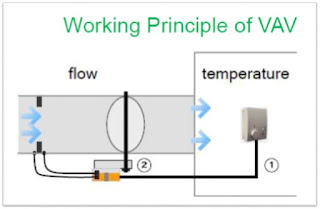
VAV means Variable Air Volume , this part of device is fitted inside the supply air duct on AHU unit.
Working Principle of VAV
- Temperature Control Loop (1) and Flow Control Loop (2) working simultaneously (in Cascade mode) to maintain indoor air quality.
- A VAV system maintains the air supply at a constant temperature while individual zone thermostats vary the flow of air to each space maintaining the desired zone temperature.
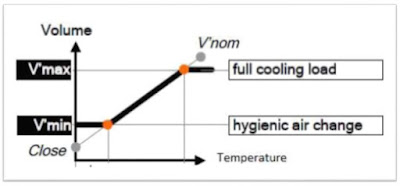
- Flow Control Loop controls the flow within the range, called as operating flow range V minimum and V maximum
V minimum: Minimal Air Change rate required to cover the
hygienic condition
V maximum : Full Load or Full Cooling Demand
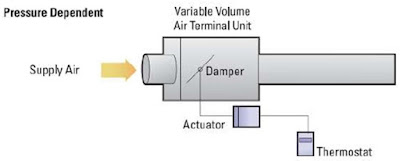
VAV - Pressure Dependent:
- A VAV is said to be pressure dependent when the flow rate passing through it varies as the system inlet pressure fluctuates.
- The flow rate is dependent only on the inlet pressure and the damper position of the terminal unit.
- The pressure dependent terminal unit consists of a damper and a damper actuator controlled directly by a room thermostat. The damper is modulated in response to room temperature only.
- Since the air volume varies with inlet pressure, the room may experience temperature swings until the thermostat reposition's the damper.
- Excessive air flow may also lead to unacceptable noise levels in the space.
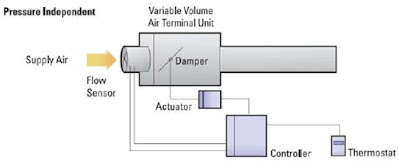
VAV - Pressure Independent
- A VAV is said to be pressure independent when the flow rate passing through it is maintained constant regardless of variations in system inlet pressure.
- The pressure independent control is achieved with the addition of a flow sensor and flow controller to the VAV box.
- The controller maintains a preset volume by measuring the flow through the inlet and modulating the damper in response to the flow signal.
- The preset volume can be varied between calibrated limits by the thermostat output.
- Pressure independence assures the proper distribution of air to the spaces that need it.
- More specifically , it allows user to feel comfortable that the design limits specified will be maintained.
- Each pressure independent terminal unit has minimum and maximum air flow limits preset at factory.
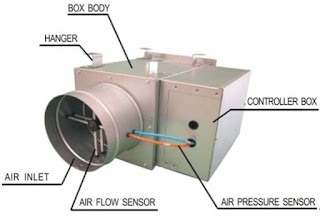 |
| VAV Box |
Maximum air flow limits prevent over-cooling and excess
noise in the occupied space.
Minimum air flow limits assure that proper ventilation
is maintained.
1. How Chiller Systems Works? (Blog)
2. How BMS System Working? (Video)
We hope this Article will helpful to you , Thank you for visit our Blog







Useful...
ReplyDeletegood topic very useful..
ReplyDeletewell clear explanation...
ReplyDelete